What does melanoma look like?
How to recognize melanoma and what to do to prevent skin cancer.
Direct Primary Care of Oklahoma is membership based health clinic committed to providing comprehensive, affordable family medicine care. You deserve a health care model that puts your needs first, we can help.
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States. One in five Americans develop skin cancer by the age of 70.
Melanoma, while less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, is a dangerous form of skin cancer because of its ability to spread rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
How dangerous is melanoma?
Melanoma is usually curable when detected and treated early. Once melanoma has spread deeper into the skin or other parts of the body, it becomes more difficult to treat and can be deadly.
Early detection makes a difference:
Finding melanoma at an early stage is crucial. Early detection can vastly increase your chances for cure.
The 5-year survival rate is 98% for patients in the U.S. whose melanoma is detected early.
The survival rate drops to 63% if the disease reaches the lymph nodes and 20% if it spreads to distant organs.
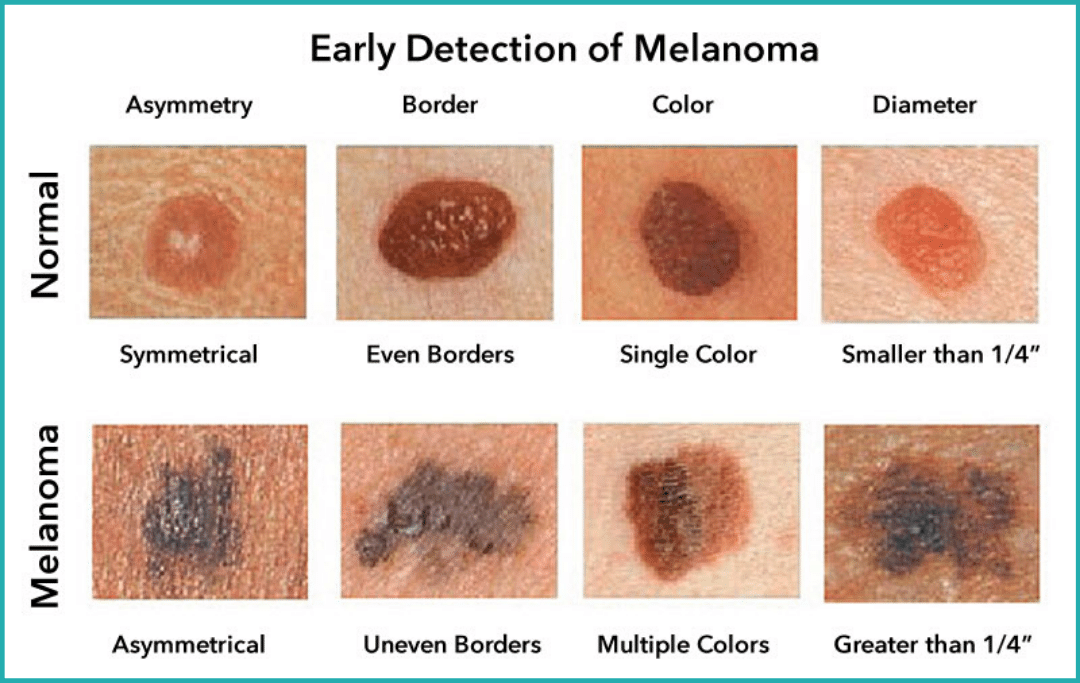
The ABCDEs for detecting melanoma:
Asymmetry - Most melanomas are asymmetrical in shape.
Border - Melanoma borders tend to be uneven or notched rather than smooth.
Color - Multiple colors (such as different shades of brown, tan, or black) are a warning sign.
Diameter - Another warning sign is a lesions that is the size of a pencil eraser (about 6mm) or larger.
Evolving - Any change in size, shape, color, or elevation of a spot on the skin, or any new symptom in it, such as bleeding, itching or crusting, may be a warning sign of melanoma.
Looking for the ugly duckling:
The Ugly Duckling is another warning sign of melanoma. This recognition strategy is based on the concept that most normal moles on your body resemble one another, while melanomas stand out like ugly ducklings in comparison. This highlights the importance of not just checking for irregularities, but also comparing any suspicious spot to surrounding moles to determine whether it looks different than its neighbors. These ugly duckling lesions or outlier lesions can be larger, smaller, lighter, or darker, compared to surrounding moles.
Melanoma Facts:
Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles.
While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
Look for anything new, changing or unusual on both sun-exposed and sun-protected areas of the body. Melanomas commonly appear on the legs of women, and the number one place they develop on men is the trunk. Keep in mind, though, that melanomas can arise anywhere on the skin.
Skin Cancer Risk Factors:
Unprotected or excessive ultraviolet (UV) exposure from the sun or tanning beds is the primary risk factor for developing melanoma and other skin cancers.
Frequent severe sunburns in early childhood can especially increase melanoma risk.
Your risk of developing melanoma doubles with a history of 5 or more sunburns.
Many other factors also play a role in increasing the risk for melanoma including genetics (family history), skin type or color, hair color, freckling and number of moles on the body.
Skin Cancer Prevention:
Seek the shade, especially between 10am and 4pm.
Avoid tanning and never use UV tanning beds.
Cover up with clothing, including a broad-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses.
Us a broad-spectrum (UVA/UVB) sunscreen with SPF of 15 or higher for every day use and SPF of 30 or higher for extended outdoor activity.
Apply 1 ounce (2 tablespoons) of sunscreen to your entire body 30 minutes before going outside. Reapply every 2 hours or after swimming or excessive sweating.
Keep newborns out of the sun. Use sunscreen on babies over the age of six months.
Examine your skin head-to-toe every month. Remember the ABCDEs. When in doubt, get it checked out.
Have a clinical skin exam at least once a year as part of your annual physical.
Did you know?
Singer-songwriter Bob Marley died from acral lentiginous melanoma, a rare form of melanoma arising from under his toenail. This tragedy highlights the importance of examining the skin head to toe.
Get the latest health news and updates sent directly to your email for free!